 |
|
 |
 Overview of TFT-LCD modules Overview of TFT-LCD modules
Driver IC
Function of driver IC
Driver ICs are critical components of TFT-LCD panels. Driver IC receives image data and delivers precise analog voltages or currents to activate the pixels on the display. When voltage is applied to the liquid crystal within each pixel cell, the liquid crystal is bent, thereby changing the intensity of light that passes through each individual pixel. Combined with the colour filter on the front glass substrate, each pixel generates its own colours which, together with other pixels, make up the whole image on the panel.
Driver ICs for mobile phones include gate drivers and source drivers. Gate drivers turn on the transistor within each pixel cell on the horizontal row on the panel. When the transistors are turned on, source drivers will generate voltages that are applied to the liquid crystal within each pixel cell on that row for data input. The combination determines the colours generated by each pixel. Small-sized panel applications, such as mobile phones, require one source driver and one gate driver, which are integrated into a single chip due to space and cost considerations. Large-sized panel applications, such as television display or desktop monitor, normally have multiple gate drivers and source drivers which are installed separately on the panel.
Driver IC technicality
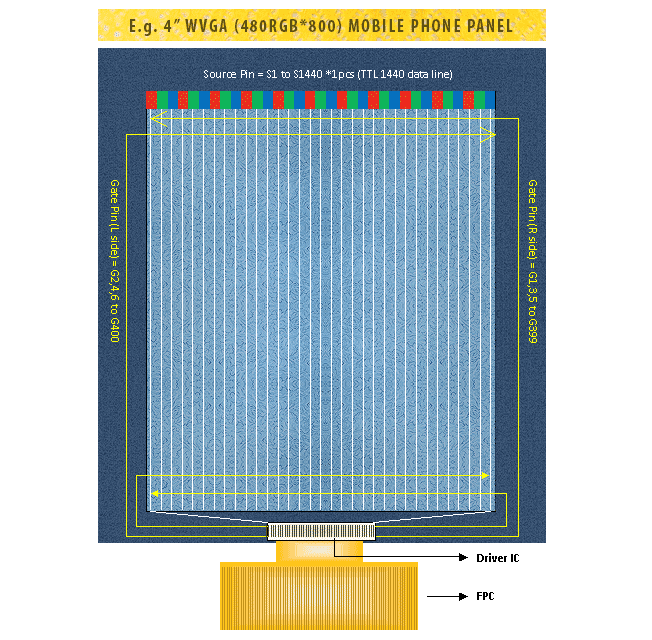
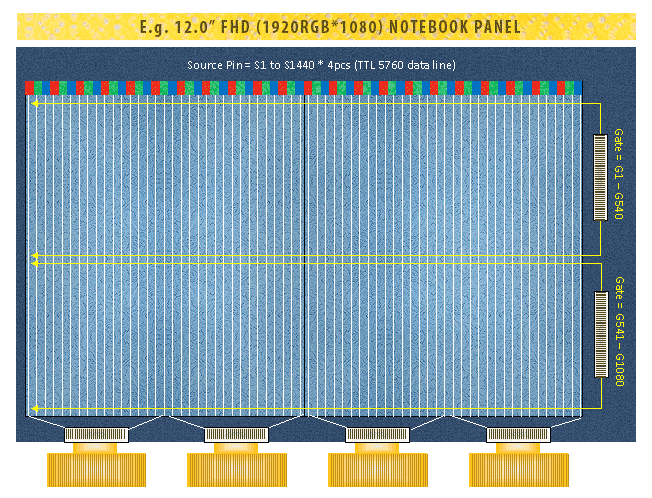
Resolution and number of channels: Resolution refers to the number of pixels in width dimension multiplied by the number of pixels in height dimension. For example, a WVGA colour display screen with 480 x 800 pixels has 1,440 pixels from side to side and 800 pixels from top to bottom, and therefore it has a total number of 384,000 pixels (480 x 800 pixels). Each pixel is a sample of an original image and more samples typically provide more accurate representations of the original image. Therefore, resolution usually determines the level of fine detail within an image displayed on a panel. Each pixel is usually made up of one red column, one green column and one blue column. These three primary colours are combined to make a wide range of colours. For example, a colour display screen with 480 x 800 pixels has 480 red columns, 480 green columns and 480 blue columns for a total of 1,440 columns and 800 rows. Therefore, the display drivers ICs need to drive 1,440 column outputs and 800 row outputs.
Colour depth: Colour depth is the number of colours that can be displayed on a screen, which is determined by the number of shades of a colour, also known as grayscale, which can be shown by panel. The number of distinct colours that can be generated by a pixel depends on the number of bits of the driver IC.
 For example, a 8-bit driver IC is capable of generating 28, or 256 different levels of voltages that are applied to the liquid crystal, resulting in different intensity of light that passes through the colour column. Thus, each red column is capable of generating 256 shades of red and each pixel (comprising three colour columns) is capable of generating 256 x 256 x 256, or approximately 16.7 million colours. Similarly, an 6-bit driver IC is capable of generating approximately 262 thousand colours. TFT-LCD panels for mobile phones currently in commercial production are normally supported by 8-bit and 6-bit driver IC and are capable of generating 16.7 million and 262 thousand colours, respectively. For example, a 8-bit driver IC is capable of generating 28, or 256 different levels of voltages that are applied to the liquid crystal, resulting in different intensity of light that passes through the colour column. Thus, each red column is capable of generating 256 shades of red and each pixel (comprising three colour columns) is capable of generating 256 x 256 x 256, or approximately 16.7 million colours. Similarly, an 6-bit driver IC is capable of generating approximately 262 thousand colours. TFT-LCD panels for mobile phones currently in commercial production are normally supported by 8-bit and 6-bit driver IC and are capable of generating 16.7 million and 262 thousand colours, respectively.

Higher level of integration: Due to the size constraint of mobile phones, the space available for components is usually limited. In order to stay competitive in the market, customers demand for higher levels of integration and simpler module assembly process to manufacture more compact panels and reduce unit costs. Small-sized panel applications require one source driver, one gate driver and timing controller which can be installed as separate semiconductors or as an integrated single-chip driver. Display driver IC manufacturers aim to offer highly integrated chips combining the source driver, gate driver and timing controller, as well as other functional circuits such as memory, power circuit and image processors, into one single chip. Due to the size and power constraints of such driver IC, single-chip driver IC is generally more complex to design.
|
|

























